1️⃣ Introduction to The Transformer Architecture
Contents
1️⃣ Introduction to The Transformer Architecture#
The entire tutorial revolves around a single architecture: the Transformer. Since its publication in 2017, the Transformer has revolutionized the field of NLP, finding successful applications in language modeling, sequence classification, sequence-to-sequence tasks such as machine translation, and many more.
As most common NLP libraries provide off-the-shelf, often pre-trained models, the actual inner working – what it is going on in the model – is often obfuscated to the practitioner.
It’s time to get our hands dirty: along the tutorial, we will implement every last bit of the Transformer and train your running implementation to solve real-world tasks.
Let’s refresh the basics#
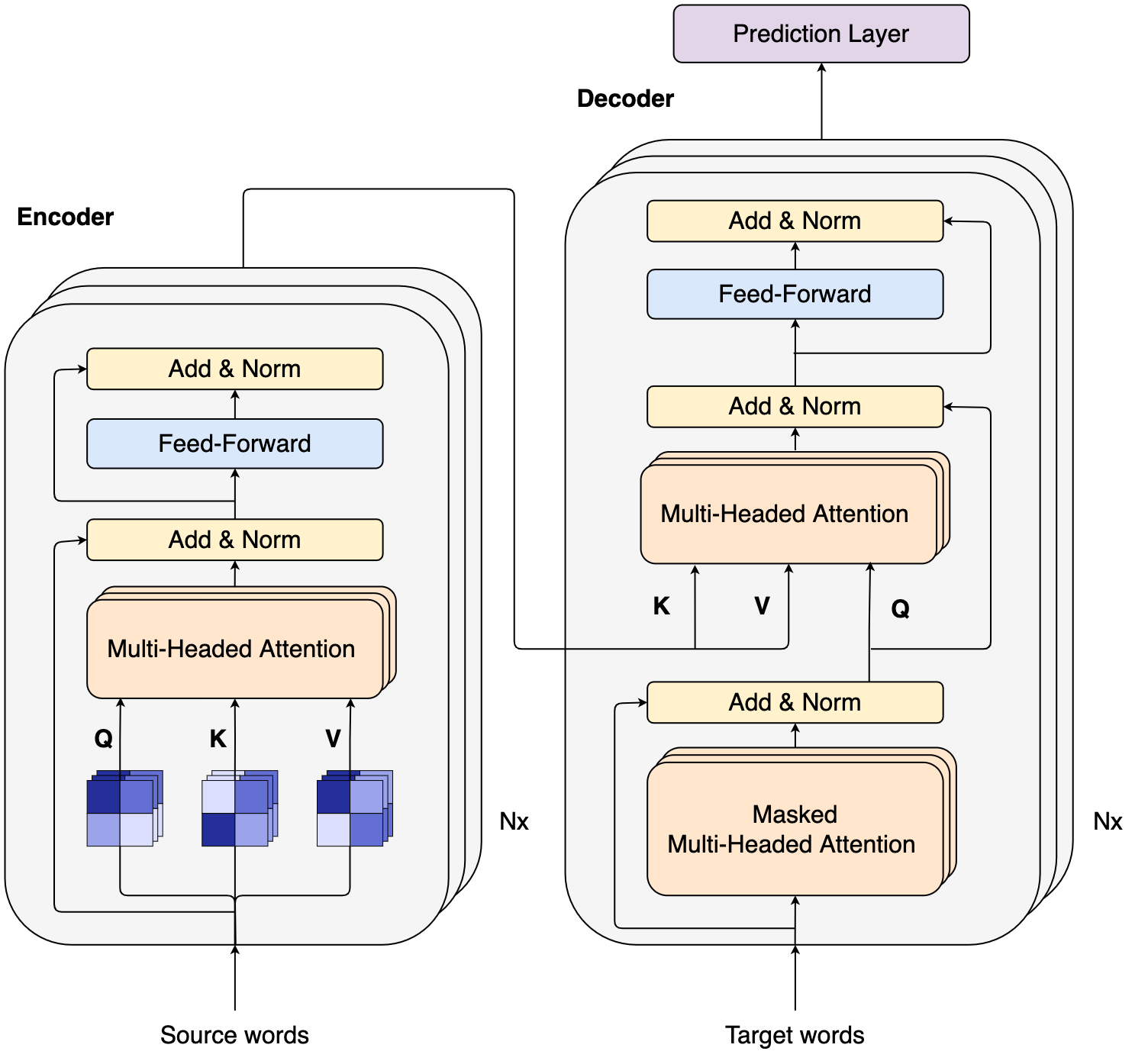
The Transformer is an encoder-decoder neural network originally devised for sequence-to-sequence tasks. Assuming that you are familiar with the notion of neural network, let’s clarify the other bits:
an encoder is a model that turns a raw piece of data into some meaningful hidden representation;
conversely, a decoder is a model that, given a hidden representation, brings the data back into the original domain;
a sequence-to-sequence task framed in the NLP domain requires learning a model that turns some sequence into another one. As you can imagine, sequences are frequently made of words.
Let’s briefly introduce the encoder and decoder and their respective core logic.
Encoder#
The goal of the encoder is to turn a list of words into a list of meaningful, dense hidden representations such that other components (e.g., the decoder or other networks) can use them.
The Transformer Encoder (Figure below, left) receives as input a sequence of items (in our case, words), often referred to as the source sequence. Then, it mixes input words using Attention, then feeds the results to a fully-connected feed-forward block with point-wise non-linear activation. Both the operations apply residual connection and layer normalization. This computation is repeated \(N\) times by identical, stacked replicas to compute the final word representations.
Decoder#
The goal of the decoder is to learn the alignment between the source and target sequences. For instance, in the machine translation task, the decoder learns what words to produce in the target language, given the words in the source language.
Like the encoder, the Transformer Decoder (Figure below, right) can receive words’ representations as inputs. During training time, it gets the target sentence to learn an association with the source.
☝️ Crucially, the decoder has two attention operations, with the first running a masked self-attention and the second one attending to the encoder output. We will give more details on that later in the tutorial.
📚 Resources#
Original paper: Attention is All you Need
Thorough guide on Transformer components: Formal Definitions in Trasformers
Practical PyTorch Transformer walkthrough: The Annotated Transform
